Foot and hand care in adulthood
Foot careThe feet have a very important role, since they not only support the body weight but also allow us to carry out daily physical activity and direct the movement of the leg muscles to facilitate mobility, in addition to maintain balance.
The feet consist of 26 bones, 32 joints, 19 muscles, and more than 100 ligaments and tendons. They are supplied by numerous blood vessels and innervated by a large number of nerves. The health of our legs and spine depends to a large extent on them, as well as contributing to a good quality of life.
The skin of the plantar area of the foot is different from that of the rest of the body: sweat glands are abundant, and there are almost no sebaceous glands or melanocytes. The epidermis is also much thicker, especially in the support areas.
During aging, the feet suffer from atrophy of the fibrofatty cells of the heel, which forces us to place excessive support on the calcaneus; At the same time, there is a decrease in the mobility of the metatarsal and tarsus joints, the result of degenerative changes in the cartilage, to which must be added a certain degree of muscular atrophy, in addition to poor circulation, which causes feel colder in the feet.
As for the nails, during aging there is less vascularity, which produces a duller and less shiny appearance. In older people, the nails are hard and brittle, and they suffer a progressive thickening of the nail plate and alterations in the matrix, which will give rise to longitudinal grooves.
Main foot conditionsConditions secondary to systemic diseasesFoot problems can be the first symptom of diseases such as arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis), diabetes and other circulatory or neurological disorders. The "diabetic foot" stands out for its socio-sanitary repercussions. It is defined as a clinical alteration of etiopathogenic and neuropathic basis induced by sustained hyperglycemia, in which, with or without coexistence of ischemia, and prior traumatic trigger, injury or ulceration of the foot occurs. The main complication of the "diabetic foot" is the appearance of gangrene, which carries a high risk of amputation. In general, "diabetic foot" infection causes few symptoms, so it is convenient to question the patient about the risk factors capable of producing it.
HyperkeratosisIt is the increase in thickness of the horny layer in areas subjected to pressure and/or friction. When pressure or friction is continued, the skin continues to develop hyperkeratotic tissue, which can cause pain. Hyperkeratotic areas are due to foot malformations or the use of inappropriate shoes. Depending on its location, a distinction is made between the following conditions: callus or heloma, hardness and rooster's eye. Calluses reach deep layers of the skin and their edges are well defined, while crow's eye is a soft callus that develops in the interdigital spaces and is produced by rubbing the fingers against each other. The hardnesses are diffuse, without defined limits and are generally located on the sole of the foot, on the heel and on the sides.
Before considering a possible treatment, it is necessary to rule out the existence of any disease (such as diabetes, vascular insufficiency, etc.) and assess whether the callus presents bleeding or is very painful; in these cases, referral to the doctor will be necessary. The most common treatment consists of reducing the keratosis by mechanical means (with manual or electric files) or chemicals (with keratolytic substances). It is essential to wear suitable shoes.
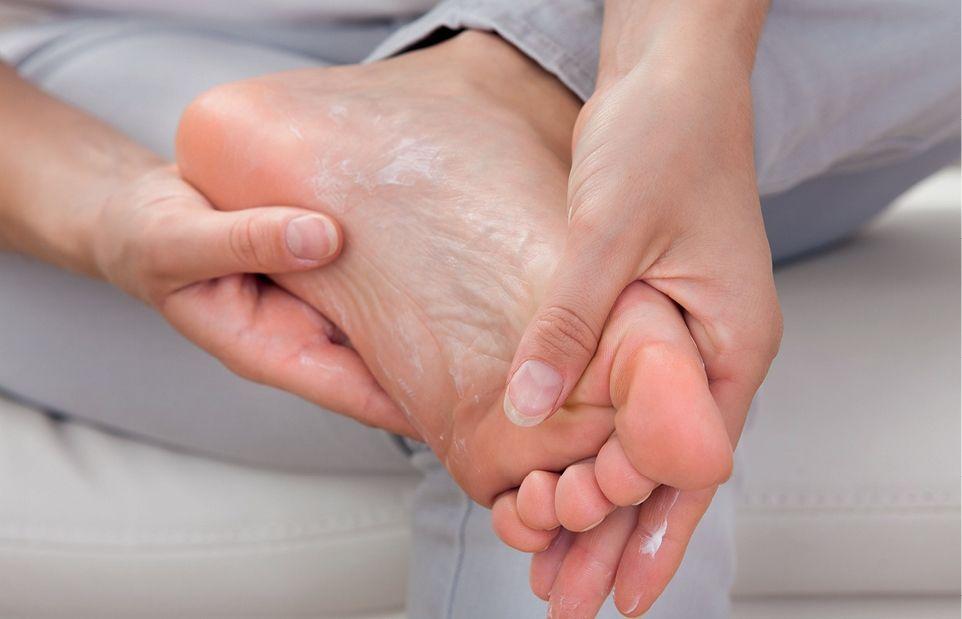
Cracks and fissuresThese conditions are small cracks in the skin that go from the epidermis to the dermis, and are located in generally dehydrated load-bearing areas (heel) or in areas with poor perspiration (interdigital spaces). The treatment consists of following daily hygiene with proper drying and hydration, and performing a weekly exfoliation.
Infectious conditions • Mycosis. The most frequent manifestations of fungal origin in the foot include the so-called athlete's foot and nail onychomycosis. Tinea pedis or athlete's foot is located on the sole of the foot and in the interdigital spaces. It is characterized by redness, intense itching, cracks, and flaking of the skin in the affected area. It is easily spread, so prevention is very important by avoiding walking barefoot in common wet areas. Pharmacological treatment includes the application of topical antifungals (imidazoles) and, among the hygienic measures, the use of shoes that allow perspiration is recommended. • Onychomycosis. It is a fungal infection of the nail where there is involvement of the nail keratin. The affected nails appear thickened, deformed and stained, to which must be added a greater fragility with respect to the healthy nail. Pharmacological treatment includes the use of topical lacquers; if the involvement is severe, systemic treatment is also associated. In case of severe involvement of the nail plate and difficulty in differential diagnosis, the patient should be referred to the doctor. Among non-pharmacological measures, it is very important to have good personal hygiene (use 100% cotton socks and breathable, non-occlusive footwear) and avoid repeated nail trauma.
Here's How to Prevent Your Dog From Getting a Bad Sunburn https://t.co/j2DZoCOlXf https://t.co/9BGG1QMKhQ
— Apartment Therapy Sun Jun 24 20:33:07 +0000 2018
Osteoarticular alterations • Hallux valgus. The hallux valgus or bunion is a deformity in the first toe with lateral exit of the metatarsus. Its origin can be found in hereditary factors, inflammatory rheumatism or foot conditions such as flat feet and cavus feet. The most characteristic symptom is pain over the medial eminence or bunion.
Treatment consists of relieving foot pain, wearing night splints, and shoes with enough room in the forefoot, flexible, and seamless in the area. • Hammer toe. It is the claw-shaped deformity of the fingers. It is due to shortening of the flexor ligaments of the fingers. Treatment consists of protecting the finger to avoid rubbing, silicone correctors or surgery, depending on the severity of the case. • Dewclaws. They are calcium deposits that are located in the bones of the feet (usually the calcaneus). The use of personalized orthopedic insoles, the use of suitable shoes, etc. is recommended. • Painful syndrome of the calcaneal pad. During aging, the calcaneal fat pad undergoes a process of progressive degeneration, which is why the calcaneus has to withstand greater pressure, triggering an inflammatory process. Predisposing factors include prolonged bearing of body weight, walking on hard floors, and obesity. The treatment goes through the use of templates, better made to measure than standard, with a correct distribution of loads.
Biomechanical alterations of the foot • Flat feet. It is characterized by a subsidence of the plantar vault, to which is added the deviation of the heel outwards with respect to the axis of the body. • Pes cavus. In this biomechanical alteration, the plantar arch has an excessive height with an overload in the heel and also in the pad and in the metatarsals of the forefoot; It usually associates claw toes due to continuous muscle traction.
There are also deviations from the sagittal axis of the body, such as foot valgus (inwards) and foot varus (outwards). All these alterations are not corrected, but it is possible to alleviate the pain and its progression with custom insoles, suitable for each need.
OsteoarthritisBone, joint and periarticular degenerative process. Among the predisposing factors are genetics, age and sex, and it is more common in women during menopause. The classic presentation of the arthritic foot is known as "triangular forefoot" (coexistence of hallux valgus and claw toes). The therapeutic goals are to reduce pain and, to the extent possible, correct deformities to improve the biomechanical functionality of the foot.
Tables 1 and 2 detail the care and preventive measures for proper foot health, both in healthy patients and in diabetics.
Hand careHands are a particularly important part of the human body, since they allow us to carry out an infinite number of functions necessary for our survival. In addition, they are responsible for the sense of touch, essential for certain people, such as the deaf and blind.
The hand has three types of bones: the wrist or carpal bones, the palm bones (metacarpals), and the finger bones (phalanges). The muscles of the forearm perform most of the movements of the hand, and the short muscles of the palm control the more delicate actions. The dermal structures of the palm of the hand are thick and resistant, with abundant sweat glands, and those of the back are fine and with few glands.
Ailments of the handsDryness and roughnessEndogenous aging, and external factors such as ultraviolet radiation, cold, environmental pollutants and other factors such as professional activity, an unbalanced diet and the consumption of tobacco and alcohol can deteriorate the condition of the skin. Aging produces a decrease in the thickness of the epidermis and the density of the dermis. It also reduces its cellular capacity and its vascularity.
To avoid the appearance of dryness and roughness, proper hygiene and hydration is recommended (Table 3).
Hyperpigmentation (age spots) These are small areas of color change (hyperpigmentation). It appears in adults over 40 years of age with a genetic predisposition. The cause is an increase in the synthesis of melanin in the epidermis. The synthesis chain has tyrosine as its substrate, which through a series of polymerization and oxidation reactions generates melanin. Although the number of melanocytes also decreases as the skin ages, those that remain increase in size and their distribution becomes more focused.
The treatment consists of eliminating the change in skin color (blemishes) with the use of chemical exfoliations (alpha-hydroxy acids) and laser. The assets used are: kojic acid, hydroquinone, derivatives of vitamin C, azelaic acid, etc.
Osteoarthritis of the handsChronic disease characterized by progressive degeneration and wear of the articular cartilage of the hands, with loss of normal mobility and deformation. It usually begins at 40-50 years of age, although there are cases of later onset. The most commonly affected joints are the trapeziometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints.
OA of the interphalangeal joints has a hereditary component. Metacarpophalangeal osteoarthritis is rare, and usually occurs in people who have carried out manual labor throughout their lives. Trapeziometacarpal osteoarthritis, also known as rhizarthrosis or thumb osteoarthritis, is more common in middle-aged women and usually occurs on both hands. In advanced cases, a deformity is seen near the wrist, and pain increases when pinching the thumb. Treatment consists of stretching exercises (in case of pain it is advisable not to force the affected joint) and daily baths of hot water or paraffin, except when there is an outbreak, in which case cold should be applied. Pharmacological treatment is based on taking analgesics in case of pain and anti-inflammatories in case of flare-ups, and the use of chondroprotective drugs (hyaluronic acid, glucosamine sulfate, diacerein, and chondroitin sulfate).
BibliographyDivins MJ. Foot care (I). Start at the base. Professional Pharmacy. 2001; 15(6): 36-46. Divins MJ. Foot care (II). The best point of support. Professional Pharmacy. 2001; 15(4): 36-40.Font E. Hand and nail care. Offarm. 2002; 21(10): 92-98.Fustero I. Foot care. Hygiene and maintenance of the most common problems. Offarm. 2007; 2: 66-72.Garrote A, Bonet R. Hygiene and care of hands and nails. Offarm. 2011; 30: 48-52. Gómez Ayala AE. Basic podiatric care. Performance. Professional Pharmacy. 2006; 6: 43-47.Puig L, Peramiquel L. Common problems of the skin of the feet. Prevention and treatment. Professional Pharmacy. 2003; 7:60-62.

![47 best antiage nutritive cream in 2022 [based on 326 reviews]](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_6/2022/2/27/1918fc37c66ad30564173e69d9df88a0.jpeg)








